The Transformative Nature of Vampirism: Two Centuries of Gothic Characterisation
The legacy of the vampire is a revealing case study, tracing the ways in which tropes and genres are influenced by societal changes and cultural trends throughout history. AM’s Victorian Popular Culture resource provides an insight into how the characterisation of vampires has evolved over the last two centuries.

Vampire, n.d., © Senate House Library, University of London. Further reproduction without permission is prohibited.
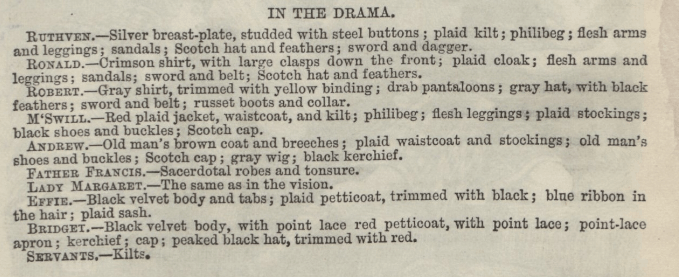
First performed in August 1820 and set in Scotland, The Vampire; or, the Bride of the Isles is a piece of theatre tellingly billed as “A Romantic Drama, in Two Acts”. Adapted from John Polidori’s The Vampyre, this play helped transform the repulsive vampire of European folklore into the aristocratic, devilishly charming character we see in popular vampire fiction today. A script of the play, digitised from the Malcolm Morely Collection at the University of London, allows contemporary readers to visualise the nineteenth century imagining of the vampire, especially through details in costume direction. Perhaps surprisingly, this staging suggests that Lord Ruthven – the titular villain – wear a plaid kilt, sandals, and a Scotch hat and feathers. A far cry from the modern vampire, who we may picture in a dress suit and cape, this design is eye-catching and overstated. However, the costume stresses the threat of the traditional vampire: its capability of integrating into high society, to seek out victims without being noticed.
Vampire, n.d., © Senate House Library, University of London. Further reproduction without permission is prohibited.
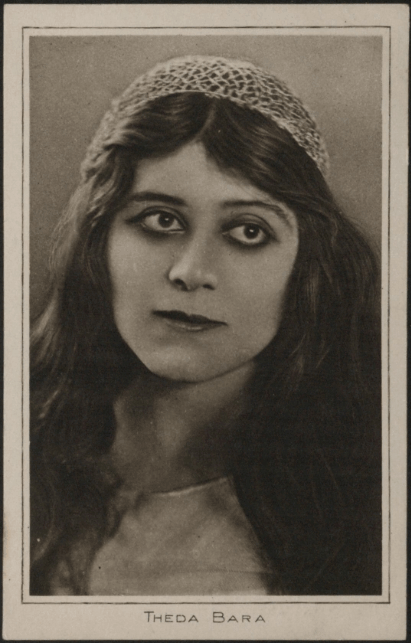

Theda Bara, n.d., © The Bill Douglas Cinema Museum. Further reproduction without permission is prohibited.
Following the publication of Bram Stoker’s Dracula in 1897, the early twentieth century saw another regeneration in the popular image of the vampire. This time, the transformation can be partially attributed to one individual – the silent film actress Theda Bara, who popularised the notion of the vampire as a femme fatale. Hypnotic and enigmatic, she presented the vampire as an alluring force in films such as A Fool There Was (1915). Interviewed in Picture Plays in 1919 – a periodical digitised from The Bill Douglas Cinema Museum – Bara describes her favourite hobby as ‘overhearing definitions of a vampire’, and names her favourite flower: ‘lilies – the vampire of the flower world’. Here we see Bara incorporating fictional character traits into her public image as an actress: an indication of the sheer popularity of this particular version of the vampire.

Picture Plays, 22 Nov 1919, © The Bill Douglas Cinema Museum. Further reproduction without permission is prohibited.
The vampire is a character that transforms its victims, at best draining the subject of their youth and energy, at worst inflicting the fate of the “undead”. As we have seen, however, the vampire is equally subjected to transformation, be it in literature, on stage, or on film. Shifting from Scottish noble to femme fatale, the vampires in these sources reflect both the fears and desires of historic consumers of popular culture.
For more information about Victorian Popular Culture, including pricing, please request a demo.
Recent posts

For centuries, women participated in London’s book and print trades despite formal exclusion from the Stationers' Company. In part one of two, guest blogger Dr Helen Williams highlights what the Company's archives, digitised in Literary Print Culture, show about women’s roles as printers, booksellers, and business owners.

Discover how the Mass Observation Project evolved through the 2010s. Explore societal trends, from climate change to digital shifts, revealed through module IV. Read how researchers and the public document everyday life in a changing world.
